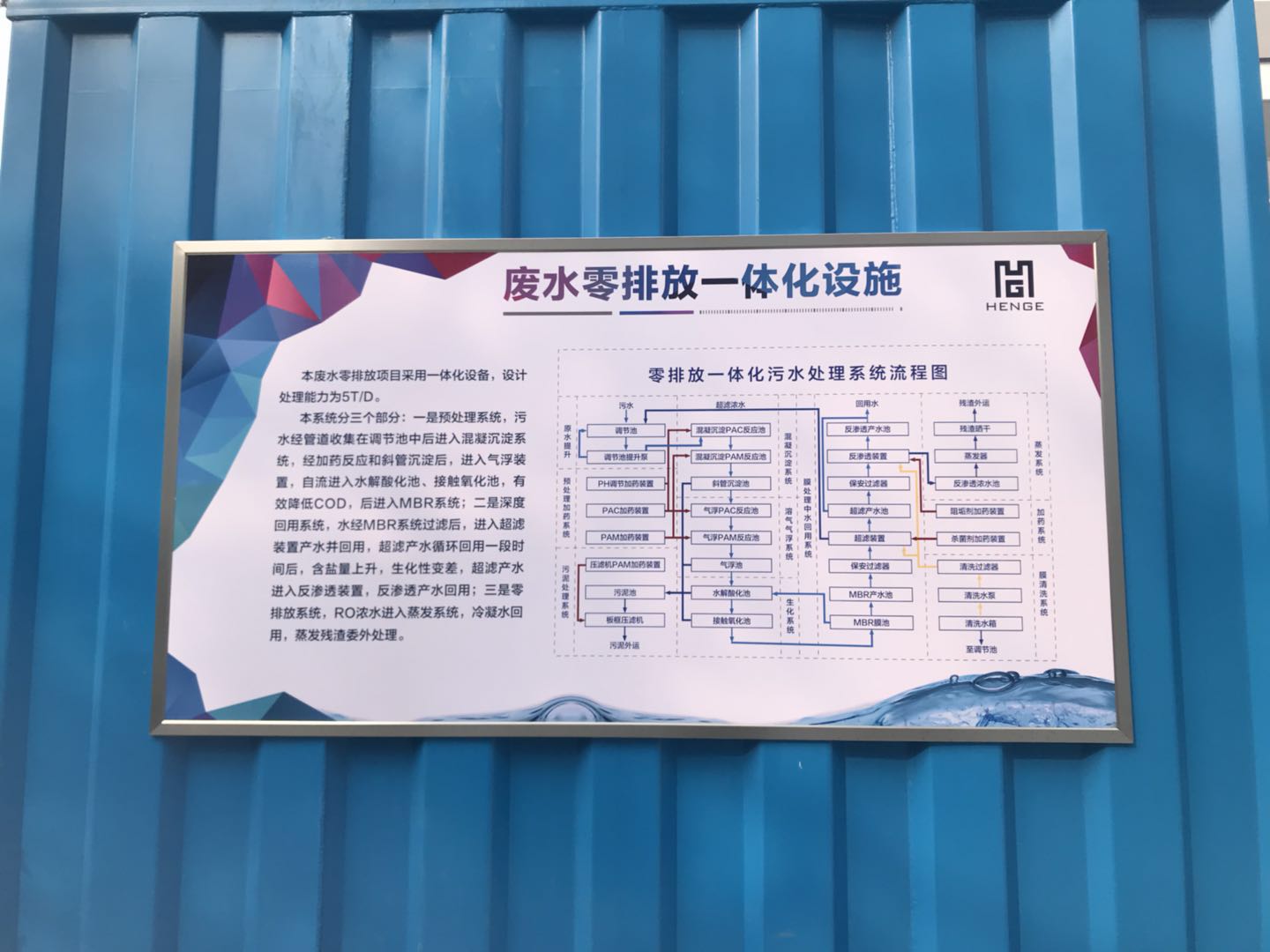
Hengguan Integrated Zero-Discharge Paint Wastewater Treatment System (Completed and Accepted in November 2017)
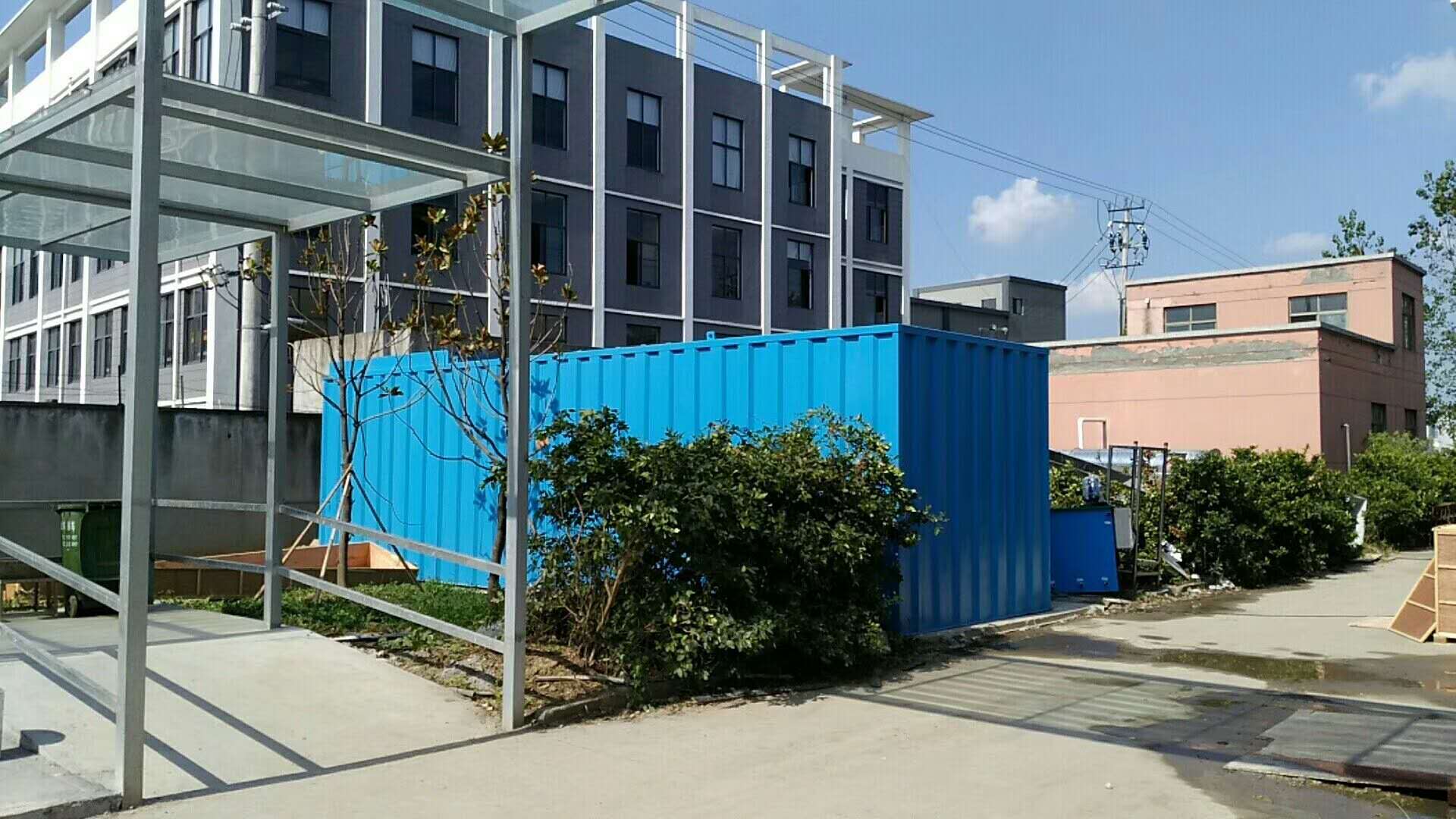

Full Process Chain Treatment Unit:
Coagulation sedimentation → Dissolved air flotation (DAF) → Hydrolysis → Aerobic treatment →MBR→Ultrafiltration→ Reverse osmosis → Evaporation, including sludge dewatering. The system treats incoming wastewater to produce reusable water and dewatered sludge, achieving actual zero discharge
Key Process Components
1. Coagulation Sedimentation: Removes suspended solids and colloidal particles through chemical flocculation[2][5].
2. Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF): Separates fine suspended solids and oils using microbubbles[5][6].
3. Hydrolysis: Breaks down complex organic compounds into simpler biodegradable forms[7].
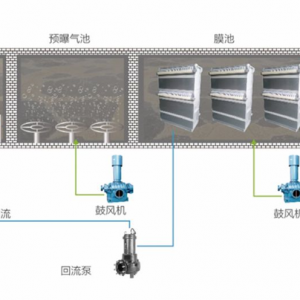
4. Aerobic Treatment: Degrades organic pollutants via microbial oxidation[1][8].
5. MBR: Combines biological treatment with ultrafiltration membranes to enhance effluent quality[1][8].
6. Ultrafiltration (UF) + Reverse Osmosis (RO): Removes dissolved salts and micro-pollutants for high-purity water recovery[1][4].
7. Evaporation: Concentrates residual brine to achieve zero liquid discharge[4].
8. Sludge Dewatering: Reduces sludge volume via mechanical compression[5][7].
Technical Advantages
- Integrated Design: Compact and modular structure suitable for industrial park applications[4][8].
- Zero Discharge: Combines advanced membrane technologies (MBR, UF, RO) and evaporation to eliminate wastewater discharge[1][3][4].
- Resource Recovery: Produces reusable water (for non-potable purposes) and stabilized sludge (for safe disposal)[3][7].
Operational Performance
- Treatment Capacity: Adaptable to variable influent loads (e.g., COD: 500–5000 mg/L)[5][6].
- Energy Efficiency: Optimized energy consumption through process integration[4][8].
- Compliance: Meets stringent industrial wastewater discharge standards (GB 8978-1996)[3][5].
Note: This system exemplifies the application of integrated physicochemical-biological-membrane processes in achieving zero liquid discharge for high-pollution-load industrial wastewater[1][3][4][7].











 苏公网安备 32050902101529号
苏公网安备 32050902101529号 Scan WeChat QR to Follow
Scan WeChat QR to Follow